Oral cavity cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the mouth (known as the oral cavity). The oral cavity includes the lips, the inside lining of the lips and cheeks (buccal mucosa), the teeth, the gums (gingiva), the front two-thirds of the tongue, the floor of the mouth below the tongue, the bony roof of the mouth (hard palate), and the small area behind the wisdom teeth (retromolar trigone).
Cancer of the oral cavity is one of several types of cancers grouped in a category called head and neck cancers. Tobacco and heavy alcohol use are two primary factors that increase the risk of developing lip and oral cavity cancer.
Most oral cavity cancers start in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the lips and oral cavity. These are called squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer cells may spread into deeper tissue as the cancer grows.
Learn more below about what to look for and what types of treatments are available for oral cavity cancer.
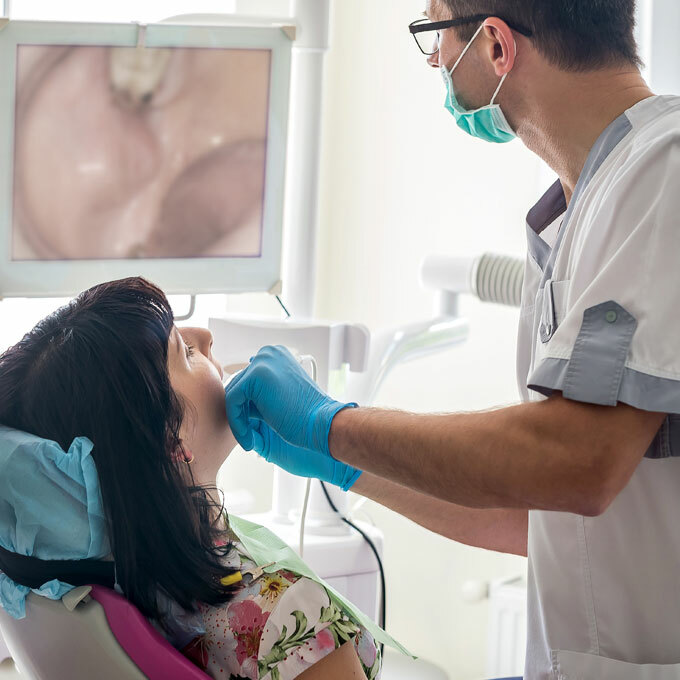
If your doctor suspects oral cancer, he or she may do further examinations and perform some tests to see if there are signs that cancer is developing.
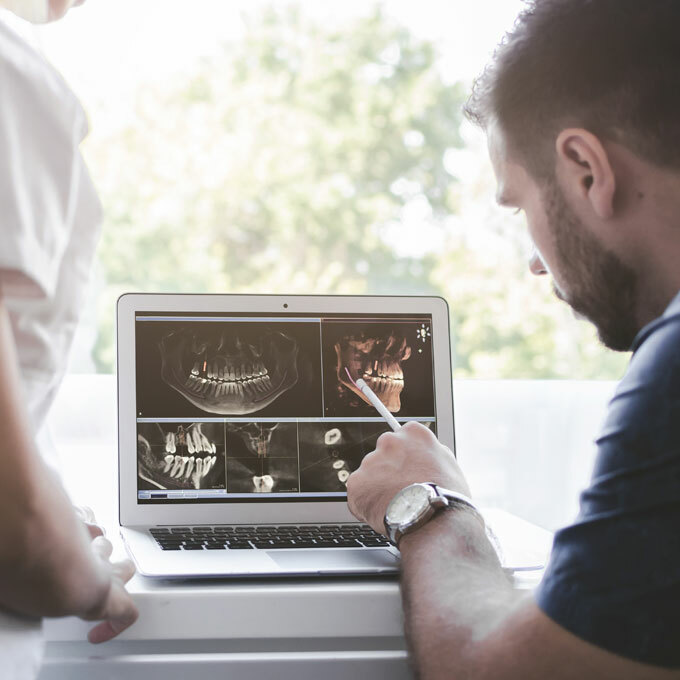
After an oral cancer diagnosis, the next step will be to determine the stage (extent).
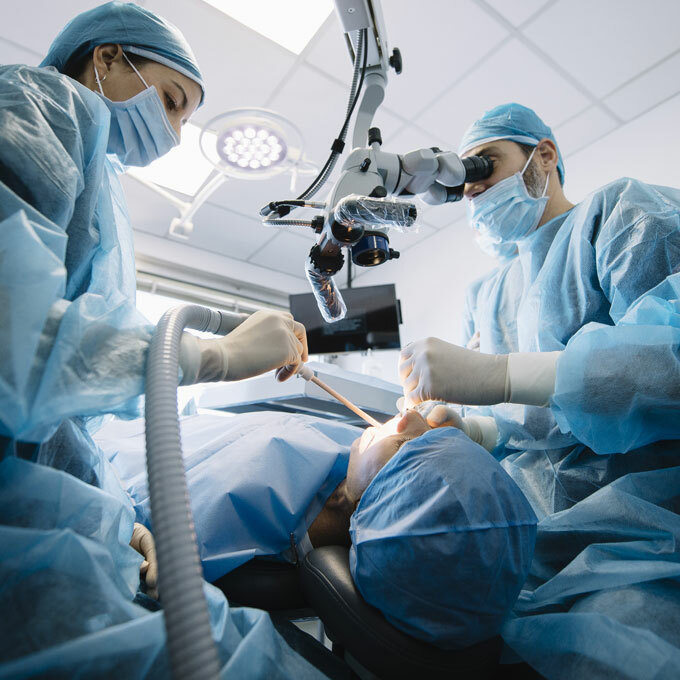
Various treatments are available for patients with oral cavity cancer.
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by lip and oral cavity cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor or your dentist if you notice any of the following:
A sore on the lip or in the mouth that does not heal
A lump or thickening on the lips or gums or in the mouth
A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth
Bleeding, pain, or numbness in the lip or mouth
Change in voice
Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit well
Trouble chewing or swallowing or moving the tongue or jaw
Swelling of the jaw
Sore throat or feeling that something is caught in the throat
Not everyone will experience symptoms. In some cases, oral cavity cancer may be found during a regular dental exam.

Quickly and efficiently build the materials you need to support your inbound marketing strategy. Drag and drop building blocks including testimonials, forms, calls-to-action, and more.